calicocloud-aks-workshop
Module 2: Configuring demo applications
Goal: Deploy and configure demo applications.
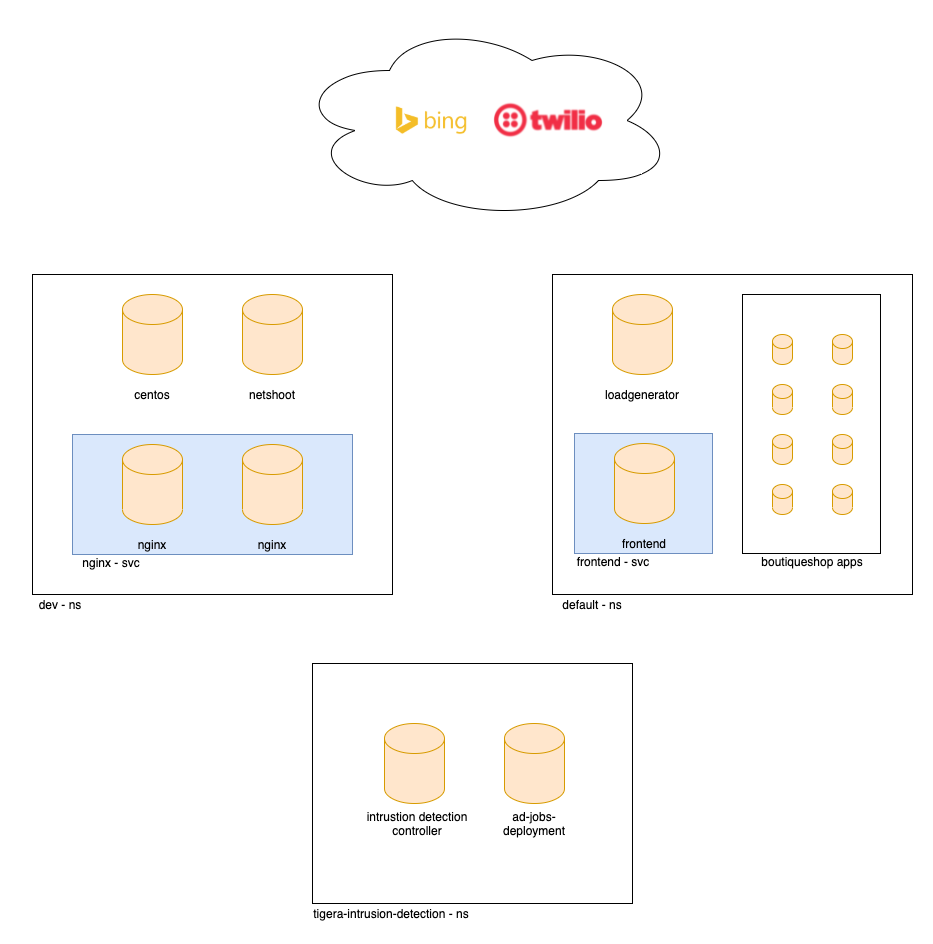
This workshop will deploy Namespace dev where several pods will be created to demonstrate connectivity within the Namespace and cross-Namespace to the default Namespace where the Boutiquestore (Microservices) Demo apps will be deployed. We will use a subset of these pods to demonstrate how Calico Network Policy can provide pod security and microsegmentation techniques.
In Module 9 we introduce Namespace tigera-intrusion-detection which contains specific Calico pods to run the Anomaly Detection engine.
Steps
-
Confirm your current folder is in this repo.
/home/azure/calicocloud-aks-workshop -
Deploy policy tiers.
We are going to deploy some policies into policy tier to take advantage of hierarcical policy management.
kubectl apply -f demo/tiers/tiers.yamlThis will add tiers
security,platformandapplicationto the aks cluster. -
Deploy base policy.
In order to explicitly allow workloads to connect to the Kubernetes DNS component, we are going to implement a policy that controls such traffic.
kubectl apply -f demo/10-security-controls/base-policies.yaml kubectl apply -f demo/10-security-controls/allow-kube-dns.yamlThis will add
allow-kube-dnspolicy to yourplatformtier. -
Deploy demo applications.
# deploy dev app stack kubectl apply -f demo/dev/app.manifests.yaml # deploy boutiqueshop app stack kubectl apply -f demo/boutiqueshop/app.manifests.yaml#confirm the pod/deployments are running. Note the loadgenerator pod waits for the frontend pod to respond to http calls before coming up and can take a few minutes. Eventually, the status of the pods in the default namespace will look as follows: kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE adservice-85598d856b-7zhlp 1/1 Running 0 113s cartservice-c77f6b866-hmbbj 1/1 Running 0 114s checkoutservice-654c47f4b6-l6wlk 1/1 Running 0 115s currencyservice-59bc889674-2xh2q 1/1 Running 0 114s emailservice-5b9fff7cb8-f49gk 1/1 Running 0 115s frontend-77b88cc7cb-btssz 1/1 Running 0 115s loadgenerator-6958f5bc8b-6lfrz 1/1 Running 0 114s paymentservice-68dd9755bb-ddqd2 1/1 Running 0 114s productcatalogservice-557ff44b96-88f7w 1/1 Running 0 114s recommendationservice-64dc9dfbc8-rwzdq 1/1 Running 0 115s redis-cart-5b569cd47-6mstt 1/1 Running 0 114s shippingservice-5488d5b6cb-l79nw 1/1 Running 0 114s kubectl get pods -n dev NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE centos 1/1 Running 0 48s dev-nginx-754f647b8b-99fsn 1/1 Running 0 48s dev-nginx-754f647b8b-hlrw8 1/1 Running 0 48s netshoot 1/1 Running 0 48sThe pods will be visible in “service graph”, for example in
defaultnamespace. This may take 1-2 mins to update in Service Graph. To view resources in thedefaultnamespace click on theService Graphicon on the left menu which will display a top level view of the cluster resources: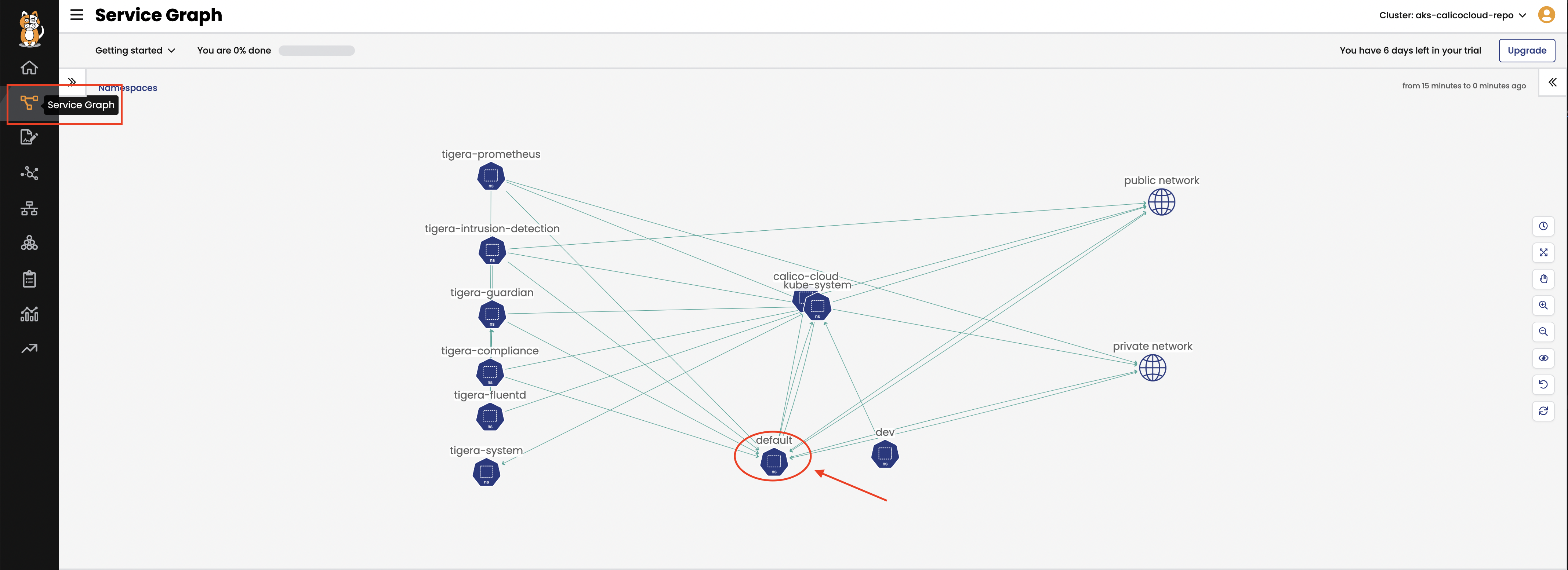
Double click on the
defaultNamespace as highlighted to bring only resources in thedefaultnamespace in view along with other resources communicating into or out of thedeafultNamespace.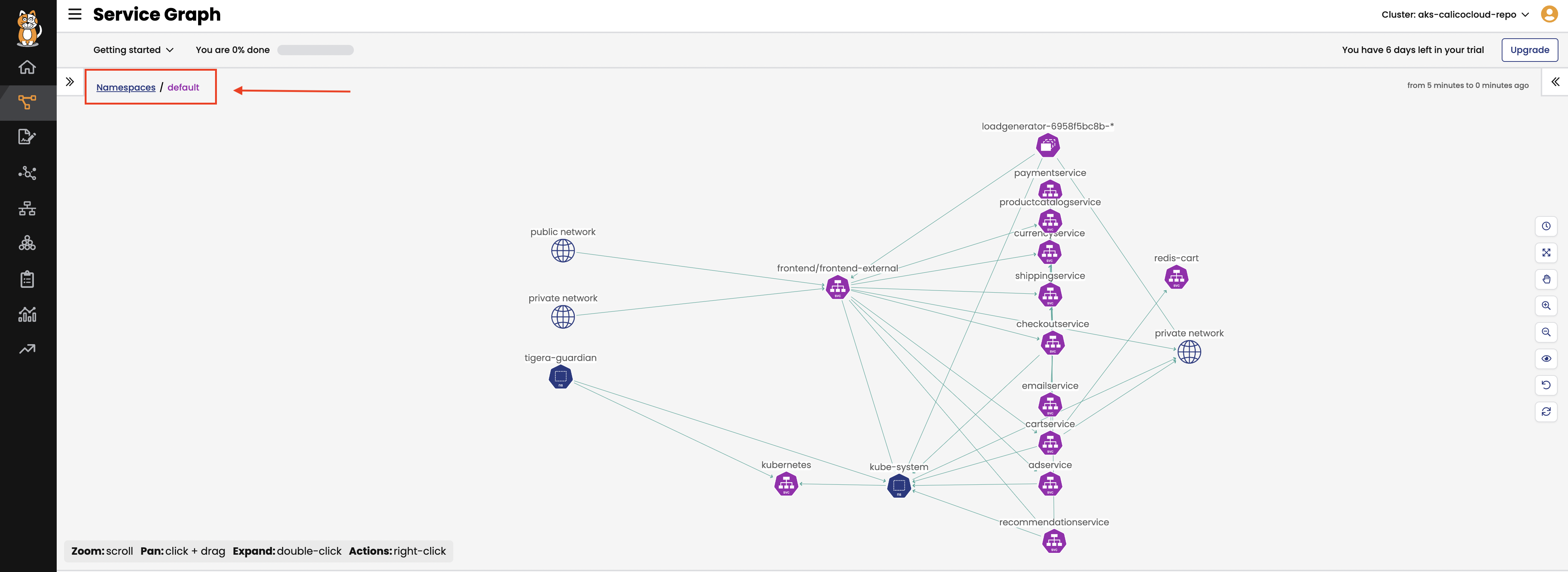
Note that pod/resource limits on your nodes may prevent pods from deploying. Ensure the nodes in the cluster are scaled appropriately
-
Deploy compliance reports.
The reports run as cronjob and will be needed for one of a later lab.
kubectl apply -f demo/40-compliance-reports/daily-cis-results.yaml kubectl apply -f demo/40-compliance-reports/cluster-reports.yaml -
Deploy global alerts.
The alerts will be explored in a later lab. Ignore any warning messages - these do not affect the deployment of resources.
kubectl apply -f demo/50-alerts/globalnetworkset.changed.yaml kubectl apply -f demo/50-alerts/unsanctioned.dns.access.yaml kubectl apply -f demo/50-alerts/unsanctioned.lateral.access.yaml -
Install curl on loadgenerator pod
Before we implement network security rules we need to install curl on the loadgenerator pod for testing purposes later in the workshop. Note the installation will not survive a reboot so repeat this installation as necessary
##install update package and curl kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get po -l app=loadgenerator -ojsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c main -- sh -c 'apt-get update && apt install curl iputils-ping -y'